机床里的合金刀头是用什么做的
粉丝22.3万获赞171.0万
相关视频
 06:06查看AI文稿AI文稿
06:06查看AI文稿AI文稿almost, everything made of metal is machined with an insert the insert has to withstand extreme, heat and force so it's made of some of the hardest material in the world, a typical insert is made of eighty percent tungsten carbide and a metal matrix that binds the hard carbide grains together where cobalt is the most common it takes more than two days to produce an insert so it's a complicated process in the material warehouse row after row of raw material are stacked the tungsten carbide we use is either recycled or comes from our own mine in austria, cobalt, titanium and all other ingredients come from carefully selected suppliers each batch meticulously tested in the lab, some recipes contain very small amounts of selected ingredients that are added by hand the main ingredients are then automatically dispensed at different stops along the way line in the milling room, the ingredients are milk to the required particle size together with ethanol water and an organic binder this process takes from eight to fifty five hours depending on the recipe the slurry is pumped into a spray dryer where hot nitrogen gas is sprayed to evaporate the ethanol on water mixture when the powder is dry it consists of spherical granules of identical sizes a sample is sent to the lab the quality check barrels of a hundred kilograms of ready to press powder arrive at the pressing machine up to twelve tons of pressure are applied depending on the type of insert the binder added in the milling room is what holds the powder together after pressing the process is completely automated each insert his weight and that certain intervals controlled visually by the operator the pressed inserts are very fragile and need to be hardened in a centering oven the process takes about thirteen hours at at a temperature of approximately one thousand five hundred degrees celsius the inserts are centered into an extremely hard cemented carbide product almost as hard as diamond the organic binder is incinerated and the insert shrinks to approximately half its original size the excess heat is recycled and used to heat the premises in winter and call them down during summer the inserts are ground one by one in different types of grinding machines to achieve the exact size geometry and tolerances as the cemented car carbide insert is so hard a disc with a hundred and fifty million small industrial diamonds is used to grind it the excess carbide is recycled as well as the oil that is used as cutting fluid the majority of inserts are coated either through chemical vapor deposition, cvd or physical vapor deposition pvd here we see a pvd process the inserts are placed in fixtures and put into the oven the thin layer of coating makes the insert both harder and tougher this is also so where the insert gets a specific color although the insert has been inspected at the lab regularly during the whole process it's manually examined again before its laser marked and packed after labeling the gray boxes are ready to be sent out to manufacture us around the world when the inserts are worn out, they are returned to sandvik corlement for recycling and the process of making a new insert begins。
268机床商务网 07:33
07:33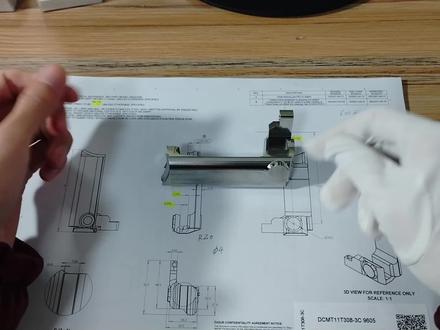 07:27查看AI文稿AI文稿
07:27查看AI文稿AI文稿上期视频呢,咱们讲了这个第二序,这个工艺台加工这个工艺台所涉及到的一些刀具,以及一些这个刀具这个加工知识。这期视频呢,咱们继续往下加工。咱们第三序呢还是用到虎钳啊,同样的,呃,虎钳 这一项呢是电铁定位, s 项呢压了一个这个平行电铁啊, s 项定位外轴呢是死枪口。这是咱们第三序的装下及定位方法。在第二代机床上呢,咱们要加工五序的内容,第三序用虎钳,剩下的四序呢都用咱们这个转接板进行加工, 嗯嗯嗯嗯嗯嗯嗯。 咱们第一把刀呢还是这个用的是快劲给啊,因为这个去除量还是比较大。 这个第一把刀呢,加工的内容还是比较多的啊,首先是把这余量去除,然后沿着这个轮廓进行分层,喜鹊还是每次零点五转速两千五,净给两千五啊。加工那个岛屿这块呢?呃,调用了三个子程序,为什么三个呢?因为第一个子程序是加工了个小岛屿, 这个小岛屿到这块呢有个台阶,这个台阶的时候呢就调用第二个子程序,沿着这个大轮廓进行粗开 铺开,到这个负的十八点多的时候呢,这有一个圆弧接刀,你就不能再切了,再切的话就把这圆弧过切了,这样呢调用第三个程序。第三个程序是干嘛呢?就是沿着这个外形把这个端面这块的余量给去除,粗开,一直给它切透了,把这个零件这块直接切透了, 把这两块的余量都给去除了,去除完以后用它给这个圆弧面进行粗开,大部分呢,这切药量呢是用这个这把快进给给它粗切了一下 十二的核心洗刀加工了,这个第一步是加工这个顶面加工这个顶面把这个尺寸加工到位,然后清洗这个侧面 这个侧臂,把这个侧臂加工出来了,然后这个侧臂和这个台阶加工到位了,然后把这个这块有个平台加工到位了, 这把刀呢是范六直径的啊,因为这大家可以看啊,这块有一个这个有一个零点五身的一个平台,这块啊这个平台,这个这个拐角呢是二二一,咱们没有直接用那个范二的洗刀加工啊,用范六的洗刀呢,沿着这个轮廓出加工了一下, 然后上了一个饭二十斤的给他做了一个青根。 现在视频中这把刀呢是用的是 fi 四 r 二的球头洗刀,因为上一把刀呢是费时期,费时期的时候你这个粗切粗切这个圆弧这块流量流的比较多啊,咱们用这个啊二的球头洗刀啊,先把这圆弧的轻点这块 给他做一个这个余量的去除,因为这个防止你这个后续这个曲面半经加工的时候呢,这个刀具突然间到这个圆弧拐角这块呢切割量特别大,所以咱们就用这个啊二的球头洗刀,在这个圆弧这个根部首先进行了一个这个余量的去除, 去除完以后把这个曲面进行那个半径加工,这三句就干完了啊,干的这个面哎,干了一个曲面,一个平台,把这个 做了一个精加工,这个豁口这块该做的都做了表面这个曲面,然后把这个进行粗加工给流了量,最后这个瓶子再加工一次,下面呢就可以上咱们这个转接板进行后续的加工了。 这个三训里边呢,有两个小知识点给大家分享一下啊。第一个呢,就是说咱们加工岛屿的时候,经加工的时候,只经加工的这一个侧比,像这个面 和这个面都没加工。为什么咱们只加工这一面,这两个面没加工呢?大家仔细看啊,因为我这个零件 最终肯定是需要立起来来加工这个面,因为你这个导点和这个台阶面你都需要把它立起来这么卡实来做一个做这个加工,你既然这个序省不掉,那这样的话,那你这个面就保留 到这一序的时候再加工,你这样的话,你的尺寸和这个衔接精度会更高一些。这个面呢,同理啊,因为这一序的时候,你这个圆弧台必须是平着下肢的时候再加工这圆弧台,那既然我这些需要平着加工,那我索性就把这个面留到 平着,掐指数,再用这个刀具进行经加工。呃,这是第一个问题啊,就是等高面在哪需加工,咱们需要考虑的问题啊。第二个小知识点呢,就是这个曲面是用那个球头加工,还是用这个侧任进行加工。这个小知识点啊,大家仔细看啊,这样呢,应该能看出来哈, 这相接部位,哎,这块有个圆弧,这块有个圆弧,这块有个圆弧,这是三段圆弧相接的。这个圆弧的加工方法呢,咱们可以在三序用这个球头洗刀啊,做这个等高外形也可以加工出来,但, 但是呢,我这块没有在这序加工,什么时候加工呢?到加工这个这序的时候,用咱们这个洗刀的一个测试 进行精修。为什么用测试不用那个圆弧这个底这进行加工呢?这一是啊,你的效率,你测试的加工效率要远远高于咱们用这个球头洗刀这个底这进行加工啊。第二个呢,你的粗糙度, 你用这个球头洗刀走这个曲面,都是仿型加工啊,都会出现这个刀纹,是吧?你这一弹一弹的,因为你走的仿型过来的,但是你用侧刃加工呢,就明显好很多,他这个粗刀度就完全要高于这个做仿型的,这可以看看啊,这是用侧刃加工出来的,非常漂亮啊。 所以说当出现这种标准的盐湖面是 r 多少 r 多少的标准的这种盐湖面,既可以用这个球头的底任加工,也可以用这个立起刀的侧任加工的时候,大家注意啊, 一定用侧刃进行加工,你这样的话效率高,哎,搓度还好,这是这个圆弧曲面啊,顺道说一点啊,刚才咱们讲的这个是圆弧面,是用底刃还是用侧刃加工? 当出现这种平面的时候,像这种小平面,当出现这种平面的时候呢,就正好相反,尽量用刀具的底刃 来加工这种平面。当你用侧任的时候,咱们这个洗刀一是容易偏摆,二是呢,他容易让刀让刀或偏摆的时候,你这个面加工完以后,和其他的面的垂直关系或平行关系就会受影响。 所以说呢,这个平面的时候呢,咱们尽量用刀具的底刃进行加工,这个呢,就是今天咱们第三序所涉及到一些知识点啊,下一句咱们就开始上这个转接板,进行第四序的加工内容。
180子山金切













